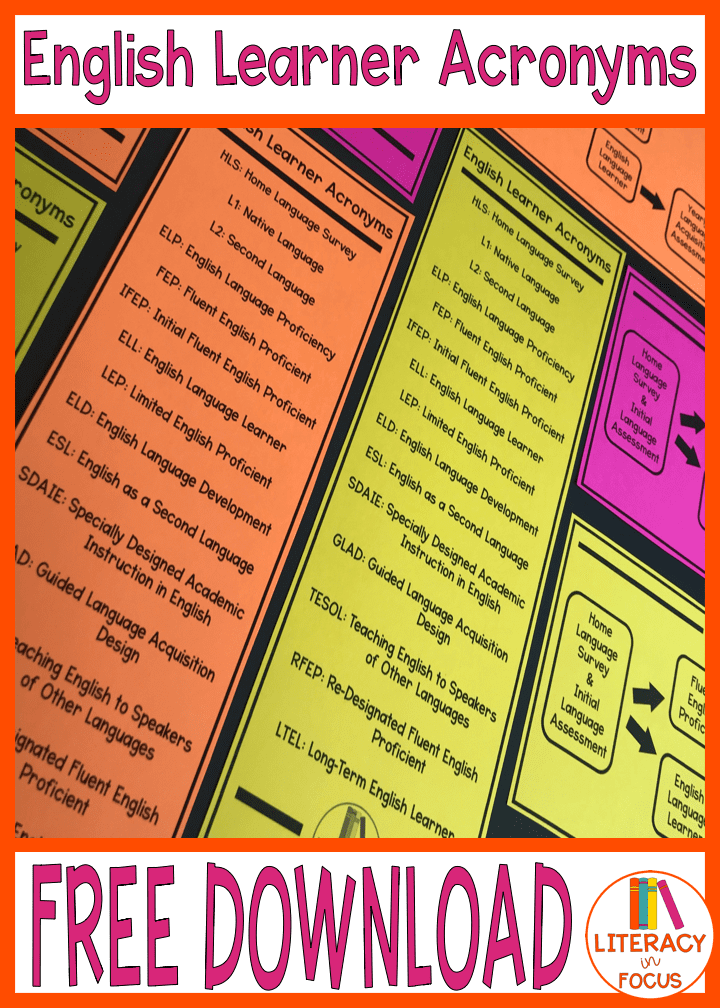
In the world of education, acronyms rule. As student diversity in the classroom increases, it is important for all teachers to have a general understanding of the acronyms associated with English learners. In this post, I hope to address and clarify a myriad of acronyms related to English learners as they move through the identification and classification processes. I have also bundled the information in a pocket reference guide you can access at the bottom of this post.
Home Language Survey
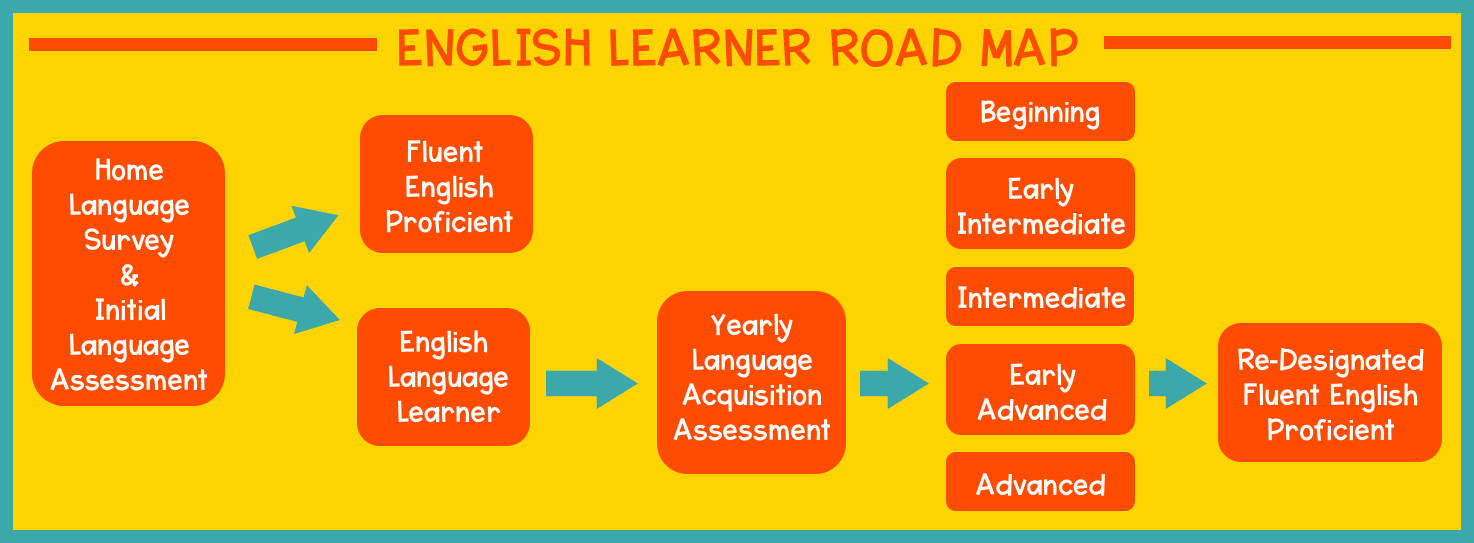
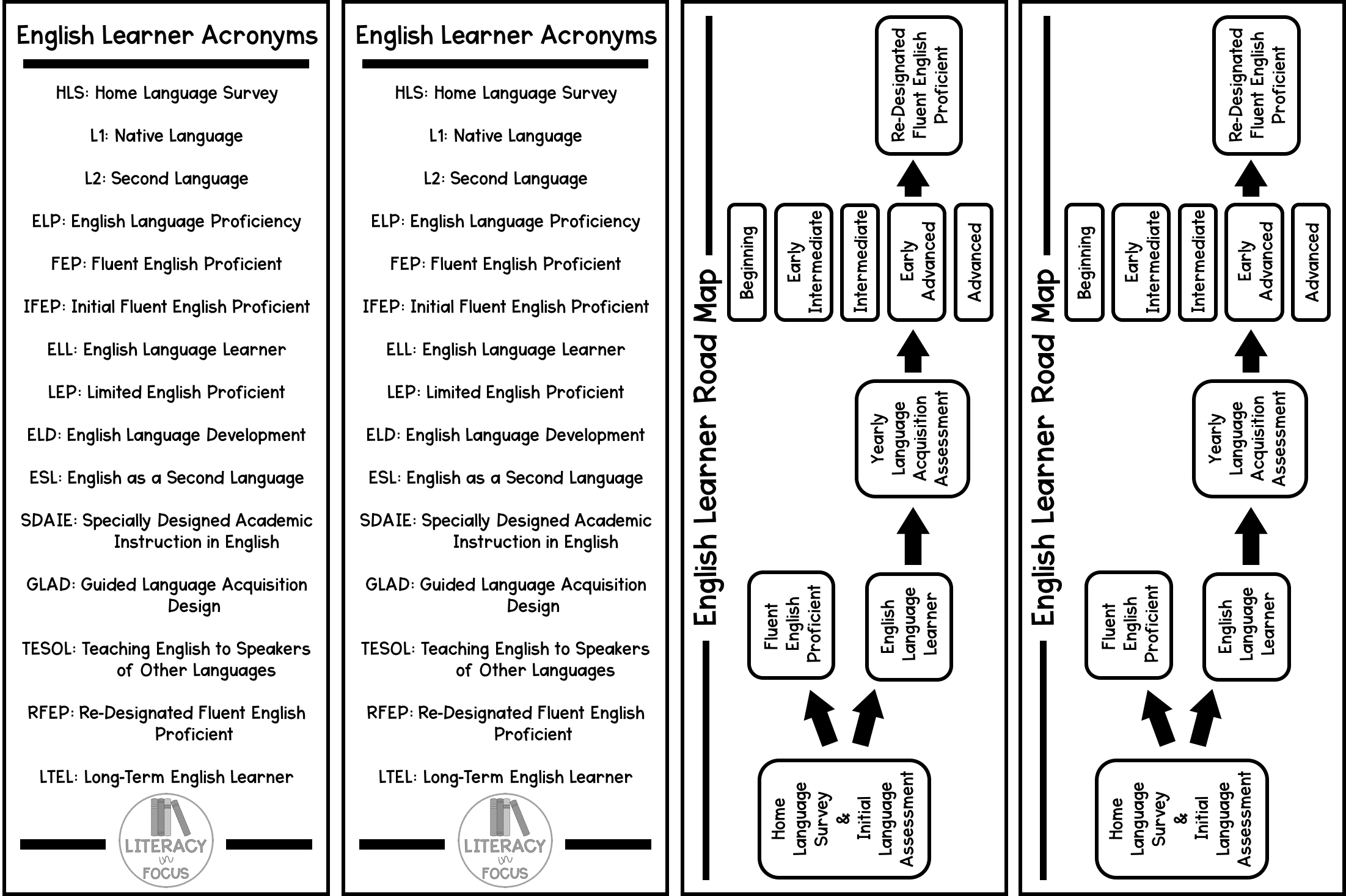
All state and local educational agencies must identify English learners in a timely manner. When a student enrolls in a new school or district, parents are required to complete the Home Language Survey (HLS), a questionnaire used for determining whether or not the student is eligible for language development services. If the parents indicate that the primary language (L1) spoken at home is not English, or the student’s first language (L1) was not English, an initial language assessment is required.
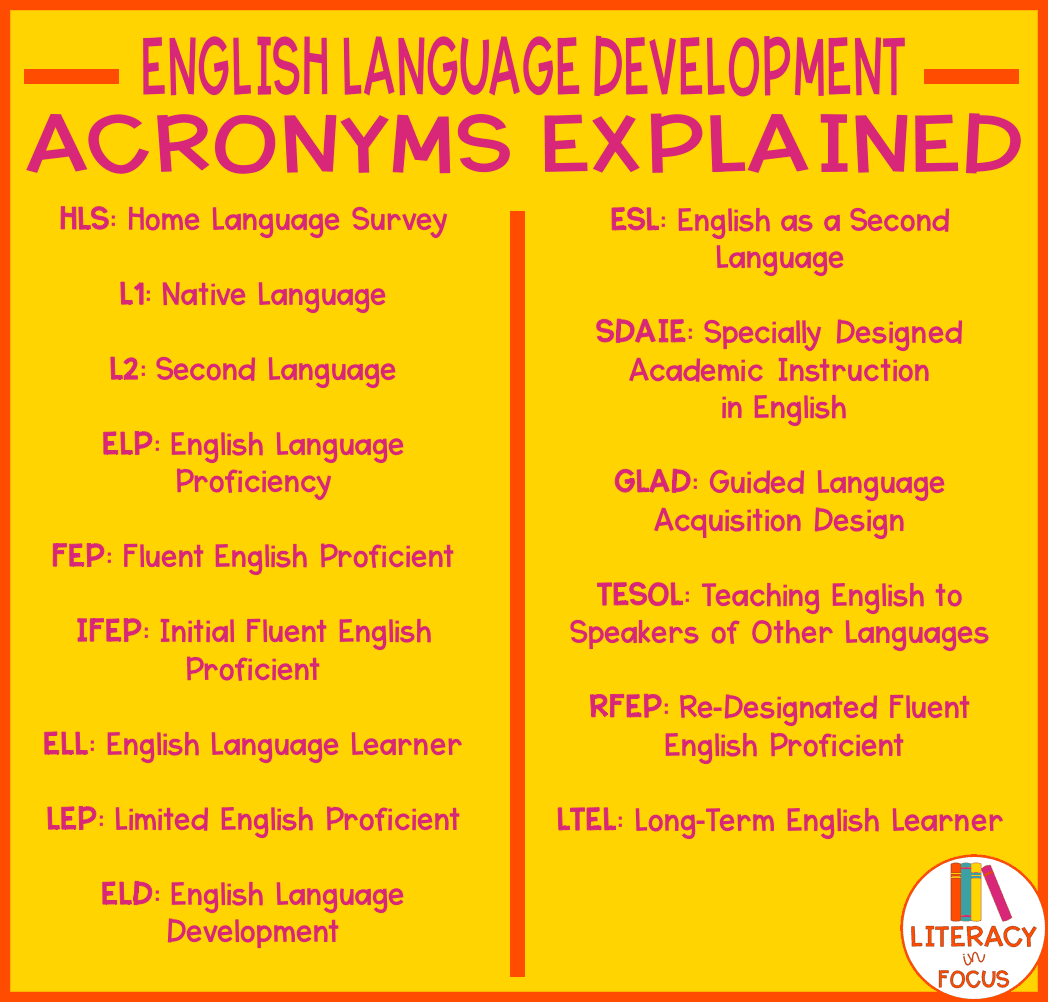
- HLS: Home Language Survey
- L1: Native Language
- L2: Second Langauge
English Learner Classifications
The initial language assessment will determine the student’s level of English language proficiency (ELP). If the student scores English proficient on the initial assessment, they are immediately identified as fluent English proficient (FEP), or initial fluent English proficient (IFEP), and language services are not necessary. If the student does not meet the criteria for fluency in English as determined by the initial assessment, they are classified as an English language learner (ELL) or limited English proficient (LEP).
- ELP: English Language Proficiency
- FEP: Fluent English Proficient
- IFEP: Initial Fluent English Proficient
- ELL: English Language Learner
- LEP: Limited English Proficient
Testing
Each year, all English language learners are assessed to evaluate their progress in learning English. Although language acquisition assessments vary by state, most testing domains include some form of listening, speaking, reading, and writing criteria. Results of the yearly language acquisition assessment indicate the student’s performance level. Performance level names and descriptions also vary by state, but there are generally five levels of language acquisition: beginning, early intermediate, intermediate, early advanced, and advanced. Also, second language acquisition does not necessarily occur in a linear fashion. An English learner may possess strong speaking skills, but fall short when it comes to reading or writing.
Teaching English Learners
Results of the yearly language acquisition assessment determine each student’s level of language development needs. Lower level students may be placed in a specific English Language Development (ELD) or English as a Second Language (ESL) class. The teacher of such classes is trained in specific strategies for language acquisition and instruction such as SDAIE (Specially Designed Academic Instruction in English) or GLAD (Guided Language Acquisition Design). Teachers of English learners either have language instruction embedded in their teaching credential or they possess a TESOL (Teaching English to Speakers of Other Languages) certificate or degree in addition to their teaching credential.
- ELD: English Language Development
- ESL: English as a Second Language
- SDAIE: Specially Designed Academic Instruction in English
- GLAD: Guided Language Acquisition Design
- TESOL: Teaching English to Speakers of Other Languages
Reclassifying English Learners
As students progress in English language abilities, the goal is for them to be reclassified from limited English proficient (LEP) to re-designated fluent English proficient (RFEP). Steps for reclassification also vary by state, but the majority of states require students to score in the early advanced or advanced levels on the state language acquisition assessment, possess passing grades in language arts and math courses, and demonstrate a general reading proficiency. Students remain in a two-year “watch window” after designating to make sure they continue to perform well without specialized services. Typically, if a student does not re-designate and remains an English learner for five or more years, they are classified as a long-term English learner (LTEL).
- RFEP: Re-designated Fluent English Proficient
- LTEL: Long-Term English Learner
Click Below to Download the FREE English Learner Acronyms & Roadmap Reference Guide
English Learner Acronyms & Roadmap Reference Guide